⚠️ Test Running in Guest Mode
Important: Your final mark will not be saved.
1.1.a. The structure and function of the skeletal system Typeit
Target Level
4-5
Running Total
0
0%
Attempt
1 of 3
Type the correct answers into the spaces. Fill all the spaces before clicking ‘Check Answers!’
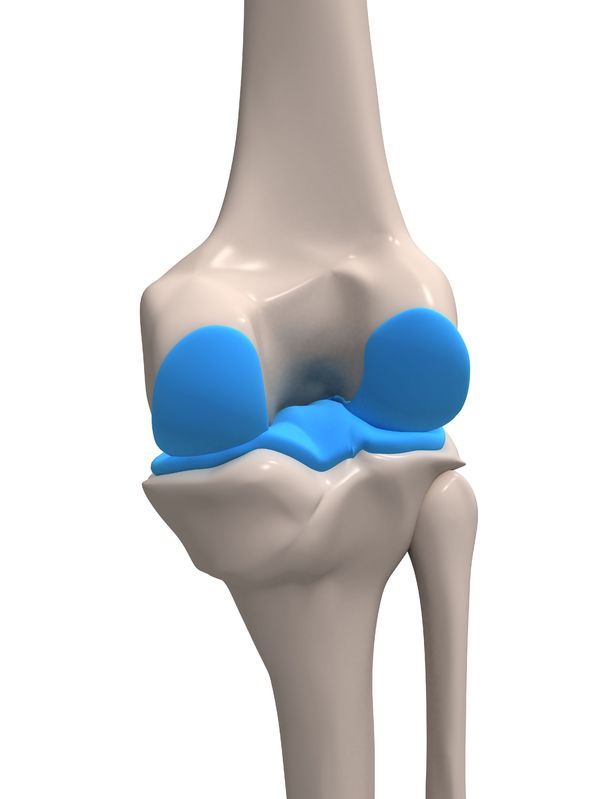
There are three types of joint in the body: fibrous (fixed), cartilaginous (partly movable) and (freely movable). There are two main types of freely movable joint to be aware of: joints (e.g. at the elbow and the knee) and joints (e.g. at the hip and the ).
The structure of freely movable joints is specifically adapted to enhancing performance and reducing the risk of injury during sport and physical activity. These structures include:
- which acts as a shock absorber and prevents bones from rubbing together
- – connective tissue which joins bone to within the joint. It strengthens and stabilises the joint and prevents it from moving further than its full range of motion.
- – connective tissue which joins muscle to bone and causes at the joint upon muscle contraction
The joints at which movement is initiated depend upon the articulating bones.
- The shoulder joint is articulated by the humerus and the .
- The hip joint is articulated by the femur and the .
- As well as the hip joint, the femur is also responsible in facilitating movement at the joint, along with the .
- Contraction of either the humerus, the ulna or the can cause movement at the joint.