⚠️ Test Running in Guest Mode
Important: Your final mark will not be saved.
1.1.1–1.1.6 The skeletal system GapFill
You must fill all the gaps before clicking ‘Check Answers!’
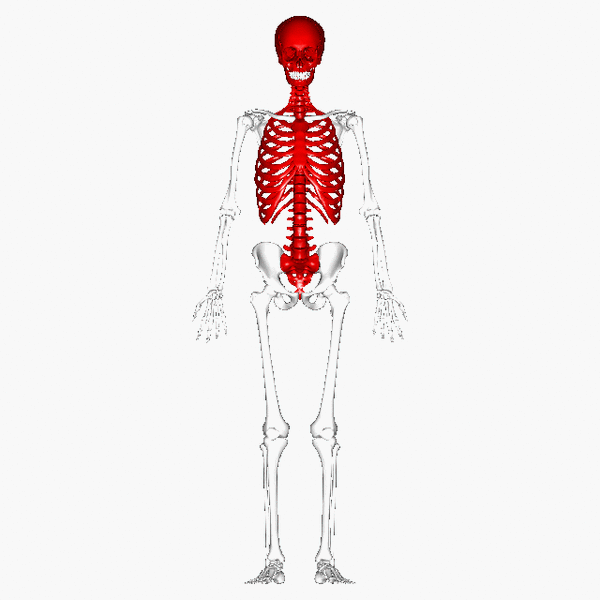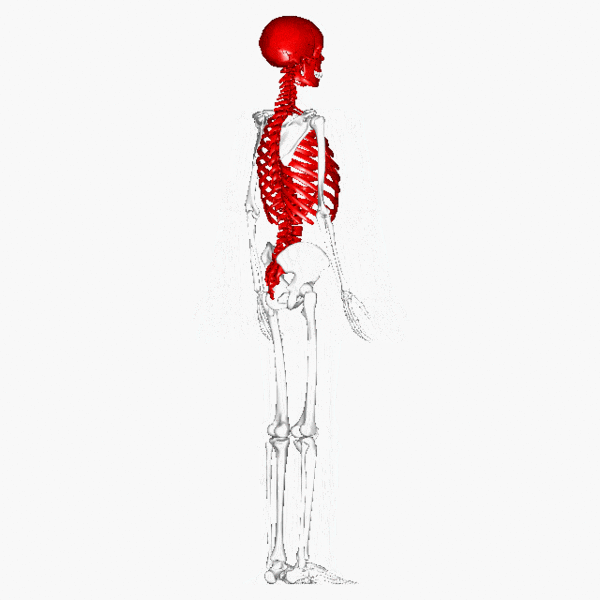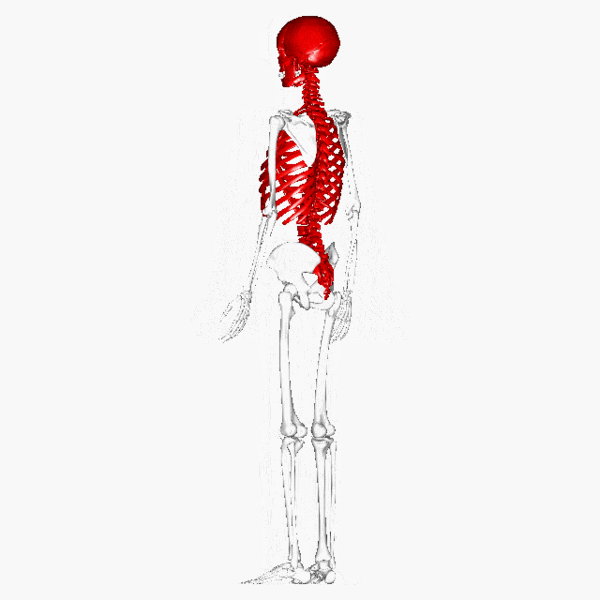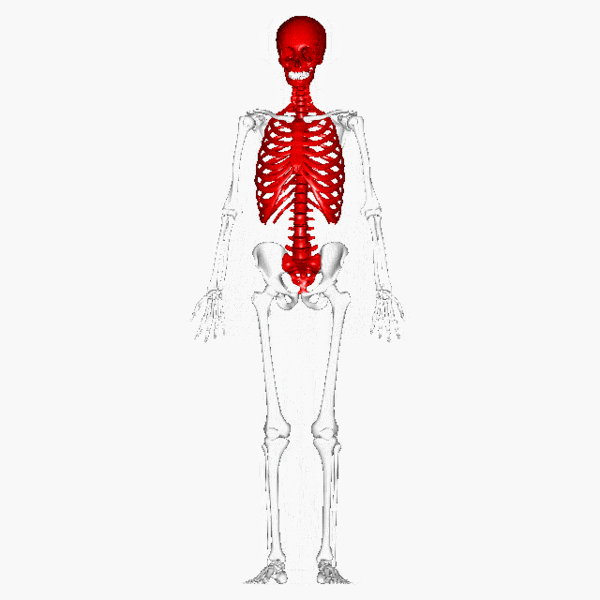
The skeletal system plays several important roles in the functioning of the human body.
Any physical activity, be that running, jumping, or throwing, would not be possible if it weren't for the functioning of the skeletal system. Neither would any sporting actions be possible, such as taking a shot in football, catching a ball in cricket, or performing a front flip in gymnastics. An important function of the skeletal system that enables these actions is the articulation of bones to form joints, which enable when working alongside the muscular system. This is achieved by flat or irregular bones providing a location for muscle via tendons. When the muscles contract, they pull on long bones, which act as levers, to allow movement of a limb. Different joint types allow for a range of movements, with joints providing a greater range of motion than joints.
The skeletal system (particularly long bones) is also responsible for the of key minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which play many important roles in the functioning of the human body. Calcium helps to increase bone mineral density and is involved in muscle contraction, whereas phosphorus is involved in energy production and tissue repair.
Flat or irregular bones that form skeletal structures, such as the cranium surrounding the brain, the surrounding the heart and lungs and the vertebrae surrounding the spinal cord, play an important role in the of vital organs, allowing them to function unharmed. This is particularly important in contact sports, such as boxing or rugby, which would almost certainly result in damage to these organs if there weren't any bone structures surrounding them.
Another function of the skeleton is performed by long bones such as the humerus in the upper arm and the in the upper leg. These contain bone marrow, which is the site for platelet and blood cell . blood cells transport oxygen to the exercising muscles during aerobic respiration, whereas blood cells are involved in the immune response to infection and disease, allowing the performer to continue exercising or training. Platelets are important in repairing damage to blood vessels by forming a clot.