Note that your final mark will not be saved in the system.
1.1.d. The structure and function of the respiratory system Typeit
Type the correct answers into the spaces. Fill all the spaces before clicking ‘Check Answers!’
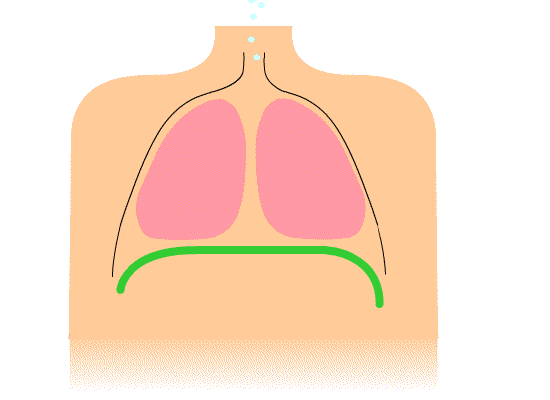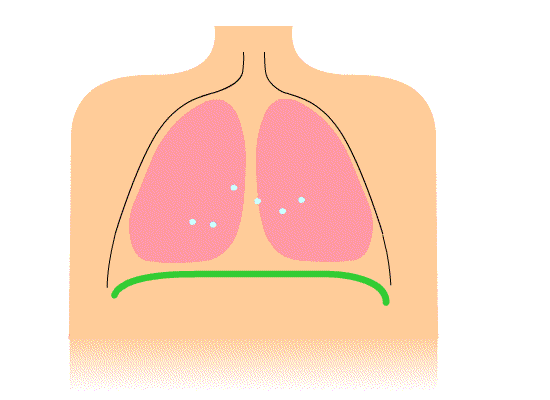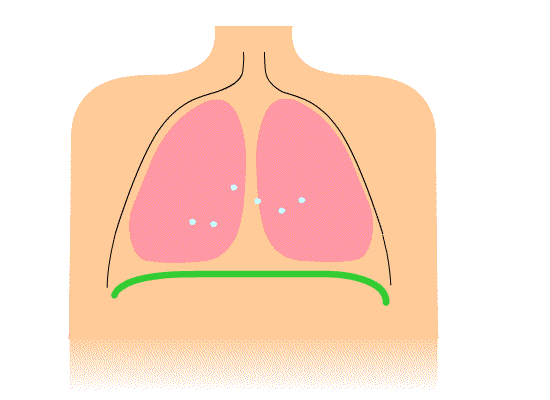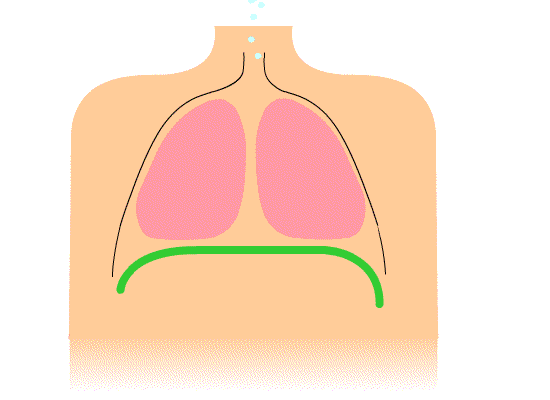
Breathing is split into two components – inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation).
When you inhale, the volume of air in the lungs increases, resulting in low pressure in the lungs. As you exhale, the volume of air in the lungs decreases, resulting in high pressure in the lungs. This relationship between volume and pressure (known as Boyle's law) is facilitated by respiratory muscles.
During inspiration, the intercostal muscles and cause the ribs to , the volume of the thoracic cavity. During expiration, the intercostal muscles , allowing the ribs to and the volume of the thoracic cavity.
The is a skeletal muscle that sits below the lungs and supports the mechanics of breathing. During , this contracts and flattens to the volume in the thoracic cavity. During , this muscle relaxes into its dome shape, the volume of the thoracic cavity.
The efficiency of the respiratory system can be monitored by the following variables:
- Breathing rate – the number of breaths taken per
- Tidal volume – the volume of air expired per
- – the volume of air expired per minute