Note that your final mark will not be saved in the system.
1.2.a. Diet and nutrition and their effect... GapFill
You must fill all the gaps before clicking ‘Check Answers!’
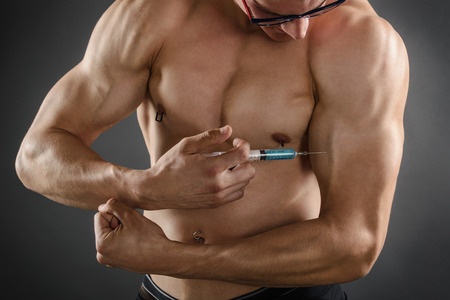
A win-at-all-costs attitude could result in athletes turning to illegal aids, which not only increase their risk of bans, fines and public scrutiny if caught, but also present various health risks. Many of the most commonly used pharmacological and physiological aids are outlined below:
Pharmacological aids - often synthetic drugs that mimic naturally occurring hormones in the body, exaggerating their beneficial effects. All those listed below are banned from use in sport by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
- steroids - These mimic the mainly male hormone and are most commonly taken in maximal-intensity sports such as weightlifting and short-distance sprint events due to their beneficial effect on enhancing muscle protein synthesis to promote growth and recovery, thus developing fitness qualities such as strength and power. Many athletes renowned for their successes have been subsequently found guilty of using this drug, including sprinters Dwaine Chambers, Marion Jones, Ben Johnson, Justin Gatlin and Tyson Gay.
- Human growth hormone (HGH) - Naturally produced by the pituitary gland below the brain, synthetic copies have an amplified effect on increasing muscle protein synthesis, reducing , and increasing cardiac output. As a result of these characteristics, it is mainly used for the same types of activity as steroids.
- Erythropoietin (EPO) - Synthetic versions are capable of further stimulating the production of and, in turn, increased haemoglobin content. This increases the oxygen-carrying of blood to working muscles during exercise, improving the efficiency of gaseous exchange at the muscle and prolonging performance before fatigue becomes limiting. Therefore, it is mostly suited to aerobic-based endurance activities such as long-distance running, cycling and swimming. A notable case in professional sport was Lance Armstrong, who was stripped of many Tour de France gold medals as a consequence of taking EPO.
Physiological aids - often used to enhance recovery time to optimise physical condition for subsequent performance. There are many legal aids but some may still seek illegal ways that could be more time-efficient, yet pose a greater health risk.
- Blood doping - Homologous blood doping involves taking blood cells from a compatible individual and injecting them, whereas autologous doping involves taking blood from the same individual, treating it by freezing, and then injecting it back into the same individual. When blood is taken from an athlete and frozen, the body compensates by generating more red blood cells. After a few weeks, the blood that was taken is injected back into the athlete, increasing the red blood cell count and thus improving oxygen-carrying capacity due to the elevated haemoglobin content. This can increase aerobic capacity in the same way as EPO and is therefore used by the same type of athletes. Indeed, it was one of the methods used by Lance Armstrong.
- hypoxic training (IHT) - This is a legal form of training which aims to replicate the beneficial effects of training by increasing the body’s response to a hypoxic environment (reduced partial pressure of oxygen). The method of IHT involves breathing hypoxic air, either using an altitude-simulated mask or chamber, while training at sea level. By stimulating red blood cell production, it has a similar effect to EPO and blood doping, albeit to a probable lesser magnitude. Therefore, it is suited for the same endurance-based activities and sports performers.
- Cooling aids - These can be implemented in a variety of forms both pre- and post-exercise. Aids such as cooling jackets and ice slushes prior to endurance-based performance help to reduce , attenuating the excessive rise when exercising in the heat, thus delaying fatigue. When a quick recovery between training sessions, competitions and fixtures is necessary, administering ice baths and cryotherapy chambers post-exercise could be effective means to reduce muscle soreness and restore contractile properties. These are commonly implemented by team sportspeople who perform on a regular basis.