Note that your final mark will not be saved in the system.
13. DNA and chromosomes GapFill
You must fill all the gaps before clicking ‘Check Answers!’
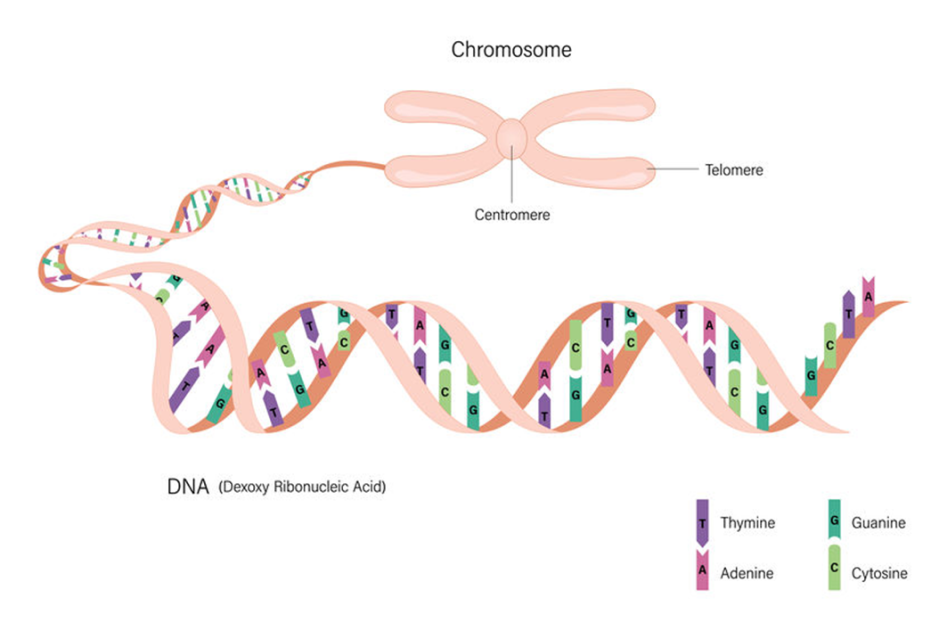
DNA and chromosomes
The genetic code for life is carried by a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.
DNA is a very long and complicated molecule. The DNA is found in the of cells.
is a long strand of DNA that contains a lot of genetic information.
is a small section of DNA that controls a single characteristic. Different ones control the development of different characteristics.
The genetic code is passed on to the next generation when organisms reproduce.
Organisms which reproduce sexually produce sex cells called . Sex cells contain half the chromosomes found in body cells.
In human beings and other animals, the male sex cells are called sperm and the female sex cells are called eggs or ova.
In plants, the male sex cells are called and the female sex cells are called ovules.
Humans have chromosomes in our body cells, arranged in pairs. We inherit one of each pair from our mother and one from our father.
The 23rd pair of chromosomes determines whether we are male or female. We call these X and Y chromosomes.
A woman has two X chromosomes, XX, while a man has one of each, XY.
All normal eggs produced by a human ovary have . In the case of sperm, however, half the sperm carry an X and half carry a Y.
A human baby's gender is determined when an egg is fertilised by a sperm. The baby will be a girl if the fertilising sperm has an X chromosome. The baby will be a boy if the fertilising sperm has a Y chromosome.
The DNA molecule has a shape like a coiling ladder, which we call a .
The rungs of the ladder are made up of pairs of chemicals called , connected to each other. It is the order of these pairs that carries the actual genetic code.
There are four different base molecules. Each is usually known by the first letter of its name:
adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) thymine (T)
The way the bases join up in pairs is fixed. A and T always join together, and C and G always join together.
Each group of three bases carries the genetic code for an amino acid. Amino acids combine together to make . The order of bases controls the types of proteins that the cell makes.