This test is run by .
Note that your final mark will not be saved in the system.
Note that your final mark will not be saved in the system.
3.1.2.5 Memory models (efficiency of information processing) Categorise
Target Level
C
Running Total
0
0%
Attempt
1 of 3
Click on an item, then click on a category to place it. Or, drag and drop the item into the correct category. Organise all items before clicking 'Check'.
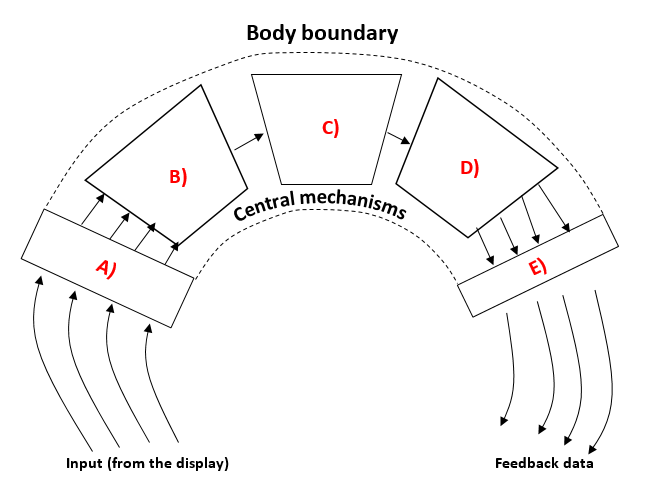
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
This processes the information gained by the sensory organs
Muscular system output data
Once a decision has been made, a message is sent via motor neurons from the brain to the muscles, to allow movement
Information is compared to previous experiences
Physical movement of the muscles
Translatory mechanism
Perceptual mechanism
e.g. a player may see (vision) or hear (sound) an attacking player approaching them
It uses selective attention to ensure relevant information is retained
e.g. a tennis player may decide to make a certain shot again as they experienced success in a similar scenario last time
The information from the display is taken in
Sensory organs
e.g. a rugby player's muscles are stimulated to allow them to sidestep a defender
e.g. a performer may filter out noise from the fans
Effector mechanism
Involves the decision-making processes